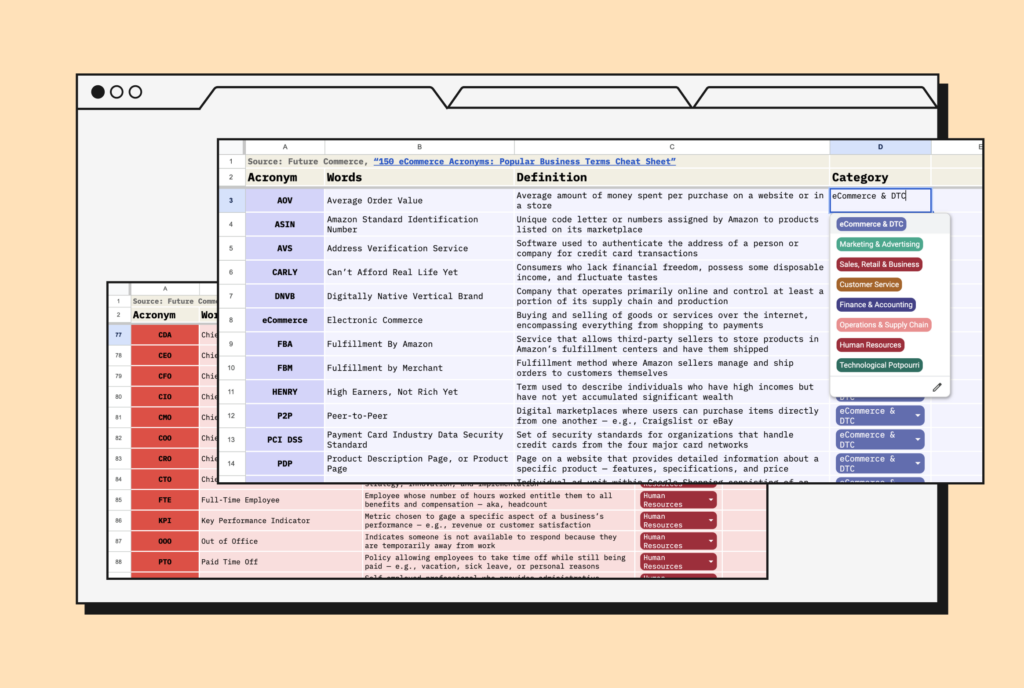
Acronyms are popular and useful for efficient communication, saving time and effort. They convey complex ideas concisely.
Acronyms help recall concepts and standardize industry documents like reports, presentations, or technical materials by condensing information into a memorable form.
Knowing idioms and acronyms is crucial for effective communication in professional settings. They help professionals quickly understand and connect with each other. While they may confuse non-professionals, they eliminate ambiguity and ensure everyone understands the intended meaning.
It’s important to use acronyms judiciously, considering the context and the knowledge level of the audience. Overuse or reliance on them without proper explanation can cause confusion. When using them, try to strike a balance and use widely understood and accessible ones.
50 commonly used business acronyms:


- API – Application Programming Interface
- AIDA – Attention, Interest, Desire, Action
- B2B – Business-to-Business
- B2C – Business-to-Consumer
- CFO – Chief Financial Officer
- CEO – Chief Executive Officer
- CMO – Chief Marketing Officer
- CTA – Call to Action
- CTR – Click-Through Rate
- CAGR – Compound Annual Growth Rate
- CRM – Customer Relationship Management
- E-commerce – Electronic Commerce
- ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning
- ETA – Estimated Time of Arrival
- FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
- FTP – File Transfer Protocol
- GDPR – General Data Protection Regulation
- HR – Human Resources
- IPO – Initial Public Offering
- ISP – Internet Service Provider
- JIT – Just-in-Time
- KPI – Key Performance Indicator
- M&A – Mergers and Acquisitions
- NPS – Net Promoter Score
- P&L – Profit and Loss
- PPC – Pay-Per-Click
- POS – Point of Sale
- R&D – Research and Development
- ROI – Return on Investment
- SEO – Search Engine Optimization
- SKU – Stock Keeping Unit
- SMB – Small and Medium-sized Business
- SOP – Standard Operating Procedure
- SaaS – Software-as-a-Service
- SWAT – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
- UI – User Interface
- UX – User Experience
- VPN – Virtual Private Network
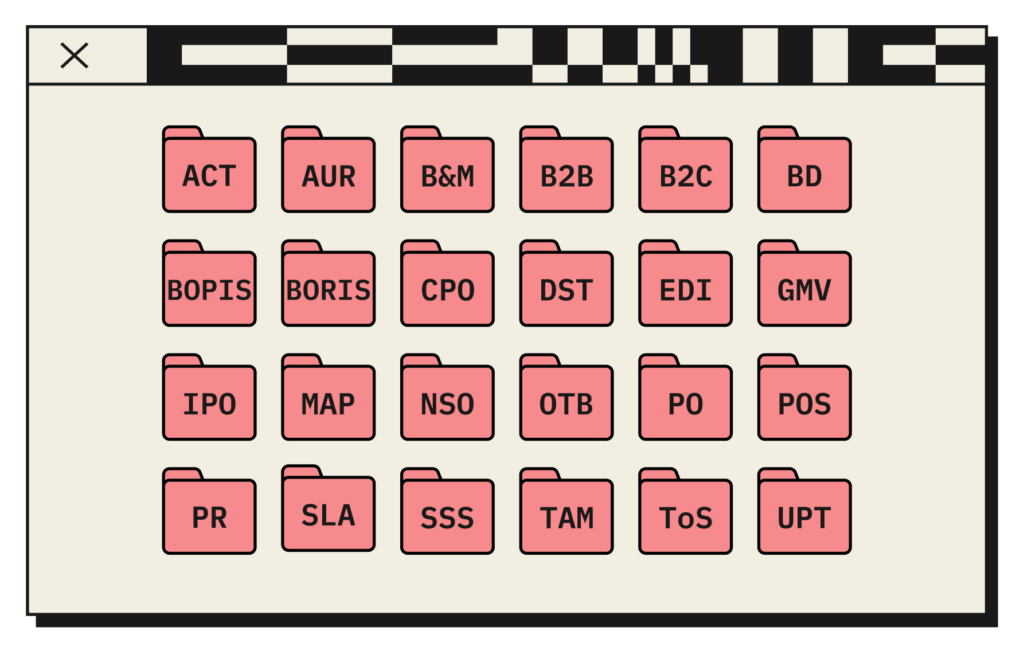
Commonly used acronyms in marketing:

1. SEO – Search Engine Optimization: The practice of optimizing web content to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results pages.
2. SEM – Search Engine Marketing: The process of using paid advertising to increase visibility in search engine results pages.
3. PPC – Pay Per Click: An advertising model in which advertisers pay each time someone clicks on their ad.
4. CTR – Click-Through Rate: The percentage of people who click on a specific link or ad, relative to the number of impressions.
5. CPC – Cost Per Click: The average cost incurred by advertisers for each click on their ads.
6. CPM – Cost Per Thousand: The cost an advertiser pays for 1,000 impressions of their ad.
7. CTA – Call to Action: A prompt or directive given to the audience to encourage them to take a specific action, such as clicking a button or making a purchase.
8. ROI – Return on Investment: A measure used to evaluate the profitability or effectiveness of an investment, campaign, or marketing effort.
9. CRM – Customer Relationship Management: A system or approach used to manage and analyze customer interactions and relationships.
10. KPI – Key Performance Indicator: A measurable value used to evaluate the success of an organization, team, or specific marketing campaign.
11. B2B – Business-to-Business: Refers to businesses that primarily sell products or services to other businesses.
12. B2C – Business-to-Consumer: Refers to businesses that primarily sell products or services directly to individual consumers.
13. NPS – Net Promoter Score: A metric used to assess customer loyalty and satisfaction based on their likelihood to recommend a product or service to others.
14. UX – User Experience: The overall experience and satisfaction a user has when interacting with a website, application, or product.
15. UI – User Interface: The visual elements and design of a website, application, or product that users interact with.
16. AIDA – Attention, Interest, Desire, Action: A marketing model that represents the stages a customer goes through in the process of making a purchase decision.
17. SMM – Social Media Marketing: The use of social media platforms to promote products, engage with customers, and drive brand awareness.
18. CTRO – Click-Through Rate Optimization: Strategies and tactics aimed at improving the click-through rate of a specific element, such as an ad or email.
19. LTV – Lifetime Value: The projected revenue expected to generate for a business over the course of the relationship with a customer.
20. ROAS – Return on Advertising Spend: A metric used to evaluate the revenue generated relative to the amount spent on advertising.
Examples of using business acronyms correctly:

- “The CEO of the company made an important announcement during the meeting.”
- “The CFO analyzed the financial data to determine the company’s profitability.”
- “The marketing team, led by the CMO, developed a new advertising campaign.”
- “Our company’s CTO is responsible for overseeing the technological infrastructure.”
- “The HR department handles recruitment and employee relations.”
- “We set specific KPIs to measure the success of our marketing campaigns.”
- “The ROI of our recent investment exceeded our expectations.”
- “Our company uses CRM software to manage customer interactions and sales.”
- “The B2B market presents unique challenges compared to the B2C sector.”
- “Our website’s FAQ section provides answers to commonly asked questions.”
- “The project manager submitted an RFP to potential vendors.”
- “Our R&D team is constantly working on innovative solutions.”
- “The company’s ROI improved significantly after implementing cost-saving measures.”
- “We rely on our CRM system to track customer interactions and improve relationships.”
- “The CMS allows us to easily manage and update our website content.”
- “The API integration streamlined the data exchange between different systems.”
- “The marketing team presented the latest KPI report during the meeting.”
- “Our employees use a VPN to securely access company resources remotely.”
- “The POS system at the retail store ensures efficient and accurate transactions.”
- “SMBs play a crucial role in driving economic growth.”
Informal acronyms you can use while texting your boss or colleagues at work:


Informal acronyms may be acceptable in certain casual or informal settings. However, generally, it’s better to use formal language and avoid informal acronyms in professional or formal emails. Despite this, you can use a few acronyms in more formal contexts because they express general concepts.
- FYI – For Your Information: This acronym is often used to provide information without expecting any immediate action or response. Because of this, it has become relatively accepted in formal communication.
- ASAP – As Soon As Possible: While ASAP is a more casual acronym, it is commonly understood and can be used in formal emails when there is a genuine urgency or time sensitivity issue.
- TBA – To Be Announced: Used when a specific event, time, or information is yet to be determined or finalized. Can be used in formal emails to indicate that details will be provided later.
- RSVP – Répondez S’il Vous Plaît: Derived from French and used to request a response from the recipient regarding their attendance or participation in an event. So, it’s widely recognized and considered appropriate for formal invitations or event planning.
Remember, exercise discretion and consider the formality of the email and the expectations of the recipient. If in doubt, it’s generally best to use complete words or phrases rather than informal acronyms in formal email communication.
How are acronyms coined?
The process of coining acronyms varies depending on the specific acronym and its origin. A few common ways acronyms are coined within the language include:
- Abbreviations: Some acronyms derive from abbreviations of longer phrases. For example, CEO comes from the abbreviation of “Chief Executive Officer,” so the combination of initial letters of each word form the acronym.
- Initialisms: In some cases, acronyms come into being by using the initial letters of the words in a phrase. But each letter is pronounced individually. For instance, CFO is an initialism derived from “Chief Financial Officer.”
- Descriptive Phrases: Acronyms can also be created from descriptive phrases that capture the essence of a concept. Like, for example, KPI, which stands for “Key Performance Indicator,” and ROI, which stands for “Return on Investment.”
- Technical Terminology: Acronyms are frequently used in technical fields and industries, where complex terms are condensed into shorter acronyms for convenience and efficiency. These acronyms are often created by taking the initial letters of technical terms or specific concepts.
- Industry-specific jargon: Some are specific to particular industries and emerge as part of the industry’s jargon and vernacular. These acronyms often evolve through common usage within the industry.




















Leave a Reply
View Comments